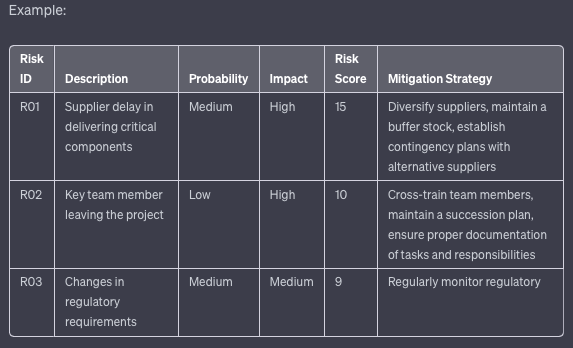
In the realm of project management, the term "project management milestone" carries significant weight. These milestones are not just markers on a timeline; they are pivotal points that signify major achievements or critical junctures in a project's journey.
Understanding the essence of a project management milestone is crucial for anyone involved in the field of project management.
This post aims to delve into the intricacies of project management milestones, shedding light on their importance and the role they play in steering projects towards successful outcomes.
The concept of a project management milestone is fundamental to project planning and execution. These milestones serve as strategic indicators, guiding project managers and their teams through the complexities of project tasks and deadlines. In essence, a project management milestone is a tool that helps in breaking down the vast and often overwhelming scope of a project into more manageable and quantifiable segments. By marking significant points on the project timeline, milestones provide a roadmap that teams can follow, ensuring that each phase of the project is completed systematically and efficiently.
The importance of a project management milestone extends beyond mere scheduling. These milestones are critical for aligning the team's efforts with the project's objectives. They offer tangible goals that the team can aim for, facilitating a sense of progress and achievement as each milestone is reached. In projects that span over months or even years, maintaining a sense of momentum can be challenging. Project management milestones address this challenge by offering clear markers of progress, keeping the team motivated and focused.
Project management milestones play a crucial role in stakeholder communication. They provide a clear and objective framework for updating stakeholders on the project's progress. This transparency is vital for maintaining stakeholder trust and ensuring that everyone involved in the project has a common understanding of its progress and challenges. Milestones also serve as checkpoints for reviewing the project's direction and making necessary adjustments to the plan.
Definition of Project Management Milestone
A "project management milestone" is a significant marker within a project's timeline, denoting a critical achievement or event. This term is vital in distinguishing it from regular tasks or activities within a project.
Project management milestones symbolise major moments or stages in a project’s lifecycle, unlike tasks that represent continuous efforts or work. These milestones are typically characterised by their nature as specific time points, rather than durations of activity, setting them apart in the landscape of project management.
Project management milestones often signify the completion of a substantial phase of work, the arrival at a critical decision point, or the achievement of a key goal. They serve as indicators of progress, providing project managers and stakeholders with tangible markers to measure how far the project has advanced.
The strategic placement of these milestones is crucial for successful project planning and execution. By defining these specific points, a project manager can create a structured roadmap for the project, guiding the team through its various stages with clarity and precision.
The practical application of a project management milestone varies across different types of projects. In a construction project, for instance, a milestone might be the completion of the foundational work or the finalisation of the architectural blueprint.
In software development, it could be the release of a beta version or the successful integration of a new feature. In each scenario, these milestones represent significant achievements that mark the transition from one phase of the project to another.
Setting a project management milestone requires careful consideration and planning. It involves understanding the project's scope, objectives, and timelines. The milestones should be realistic, achievable, and relevant to the project's goals. They should be strategically placed to provide meaningful checkpoints throughout the project, allowing for effective monitoring and evaluation of progress. Moreover, they should be communicated clearly to all team members and stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aligned and understands the significance of each milestone within the project.
The Role of Milestones in Project Management
The role of project management milestones are central to the effective management of any project. These milestones serve as vital checkpoints that help in guiding the project through its lifecycle, ensuring that each phase progresses as planned.
They are instrumental in breaking down the complex task of project management into more manageable and measurable segments, making the process more transparent and efficient.
One of the primary functions of a project management milestone is to provide a clear structure for project planning. By marking significant points in the project timeline, milestones help in setting realistic deadlines and objectives.
They allow project managers to map out the project’s journey, assigning specific goals and targets to each phase. This structuring is crucial for maintaining focus and ensuring that every team member is aware of what needs to be achieved and by when.
Beyond planning, project management milestones play a significant role in monitoring and controlling project progress. They act as indicators, enabling project managers to track whether the project is on course to meet its objectives.
This tracking is essential for identifying potential issues or delays early in the process, allowing for timely intervention and corrective actions. For example, if a milestone is not met on time, it may indicate a need to reassess the project plan or allocate additional resources to get back on track.
Communication is another area where project management milestones prove invaluable. They provide clear and objective points that can be used to update stakeholders on the project’s progress. This clarity is vital for maintaining transparency and trust among all parties involved in the project.
Regular updates centered around milestones help in managing expectations and ensuring that everyone has a common understanding of how the project is progressing.
In essence, project management milestones are more than just markers of progress; they are strategic tools that contribute significantly to the success of a project. They provide a roadmap for planning, a framework for monitoring, a platform for communication, and a mechanism for risk management. Mastering the art of setting and managing these milestones is essential for any project manager aiming to lead their projects to successful completion.
Types of Milestones
Understanding the different types of "project management milestones" is essential for effectively planning and managing a project. Each type serves a specific purpose, helping to guide the project towards its ultimate objectives.
The types of project management milestones vary depending on the nature and requirements of the project.
Each type plays a unique role in guiding the project towards its objectives:
| Milestone Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Start and End Date | These are among the most fundamental types of project management milestones. The start date milestone signifies the commencement of the project, marking the point where planning transitions into action. The end date milestone, on the other hand, indicates the project’s conclusion. These milestones are crucial as they frame the overall timeline of the project, providing clear start and finish lines for the team to work towards. |
| Key Deliverable | These milestones are associated with the completion of significant outputs or deliverables within the project. For instance, in a software development project, a key deliverable milestone could be the completion of a critical software feature. In a construction project, it might be the finishing of a major structural component. Key deliverable milestones are vital for tracking the tangible progress of the project and ensuring that key outputs are achieved on time. |
| Critical Approval | These milestones occur when crucial decisions or approvals are required from stakeholders or regulatory bodies. They are particularly important in projects that involve multiple layers of decision-making or need to adhere to specific regulations. Achieving these milestones is often a prerequisite for proceeding to the next stage of the project. |
| Financial | In projects where budget management is crucial, financial milestones play a key role. These might include the completion of a funding round, budget review meetings, or financial audits. Financial milestones help in ensuring that the project stays within its financial constraints and triggers necessary budgetary adjustments. |
| Performance Review | These milestones are set to review the performance of the project at certain intervals. They provide an opportunity to evaluate how well the project is meeting its objectives, the effectiveness of the team, and the overall project strategy. |
Setting and Managing Milestones
The process of setting and managing "project management milestones" is a critical aspect of successful project execution. This involves not only identifying key points within the project but also ensuring they are effectively managed throughout the project's lifecycle. The ability to set and manage these milestones effectively can significantly impact the overall success of the project.
The first step in this process is to identify the appropriate milestones for the project. This requires a deep understanding of the project’s objectives, scope, and deliverables.
Each milestone should represent a significant achievement or decision point in the project. These milestones should be realistic, achievable, and aligned with the project's goals. For instance, in a software development project, milestones could be based on the completion of different stages of the software lifecycle, such as design, development, testing, and deployment.
Once the milestones are set, the next step is to integrate them into the project plan. This involves assigning specific timelines and resources to each milestone. It is important to ensure that the timelines are realistic and allow for any potential delays or challenges. Effective communication is key in this phase; all team members and stakeholders should have a clear understanding of the milestones, their significance, and the plan to achieve them.
Managing these milestones involves continuous monitoring of the project’s progress against the set targets. Regular check-ins and progress reports can help in identifying any deviations from the plan. If a project is falling behind or facing unforeseen challenges, it is crucial to take corrective actions swiftly. This might involve reallocating resources, adjusting timelines, or revising strategies.
It is also important to celebrate the achievement of each milestone. Recognising these achievements can boost team morale and motivation, reinforcing the importance of the milestones and the progress being made. Celebrating these successes helps to maintain momentum and enthusiasm within the team.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Managing "project management milestones" can present various challenges, each requiring specific strategies for resolution. Recognising these challenges and understanding how to address them is essential for maintaining the momentum and success of a project.
One frequent challenge is setting unrealistic milestones, either overly ambitious or too conservative. Unrealistic milestones can lead to team stress, project delays, or a false sense of progress. The solution lies in thorough project analysis and realistic goal-setting, taking into account the team's capabilities, resource availability, and external factors.
Another common issue is insufficient stakeholder engagement or communication. Stakeholders might not fully grasp the importance of milestones or may not be sufficiently involved in the planning process. Enhancing stakeholder engagement through regular updates, involving them in milestone planning, and ensuring transparent communication can mitigate this challenge.
Misalignment of milestones with project goals is a significant obstacle. Sometimes, milestones may not reflect the project’s true objectives or may become irrelevant due to project evolution. Regularly reviewing and adjusting milestones to ensure they remain aligned with the overall project goals is crucial for addressing this issue.
Changes in project scope or external factors can also impact milestone achievement. Flexibility and adaptability in milestone management are key. Anticipating potential risks, having contingency plans, and being willing to adjust milestones as necessary are vital strategies for dealing with such changes.
Project Management Milestones Example
To demonstrate the practical application of "project management milestones," let's consider a case study in the pharmaceutical industry. Imagine a project focused on developing a new medication. This complex, multi-phase project includes:
Research
Development
Clinical trials
Regulatory approval
Product launch
The project commences with a Research phase, aiming to identify a promising compound. The completion of this phase and the selection of a viable compound is the first major milestone. This milestone is crucial, as it validates the direction of the project and sets the stage for the development phase.
Following research, the Development phase begins, involving extensive lab work and initial testing. The successful creation of a drug formulation marks the next milestone. This achievement is significant, as it transitions the project from theoretical research to tangible product development.
Next, the project enters the Clinical Trial phase. Here, a critical milestone is the completion of Phase I trials, which assess the drug's safety in humans. Achieving this milestone is vital, as it allows the project to proceed to more extensive testing in Phase II and III trials. These later phases have their milestones, each marking progress and success in demonstrating the drug's efficacy and safety.
A pivotal milestone in this project is obtaining Regulatory Approval. This milestone is achieved when the drug passes all regulatory requirements and receives approval for market release from bodies like the FDA or EMA. This milestone is a significant triumph, as it marks the transition from a developmental project to a market-ready product.
The final milestone is the successful Product Launch of the drug in the market. This includes the production, distribution, and initial sales of the medication. Achieving this milestone signifies the culmination of years of work and investment, marking the project's ultimate success.
By effectively managing these milestones, the project team can navigate the project through its various phases towards successful completion.
The concept of "project management milestones" is fundamental to the success of any project. These milestones serve as key indicators of progress, offering a structured approach to navigating through the complexities of project management. They are not merely dates on a calendar but strategic markers that signify critical achievements and decision points in a project's lifecycle. The effective use of project management milestones can significantly enhance the efficiency and outcome of a project.
How do you identify project management milestones? Let us know in the comments below.